Introduction
An ‘Apprentice electrician’ is a title assigned to an individual entering the electrical trade, having obtained formal recognition and authorization to work under supervision. It marks the initial phase of an electrician’s career, representing the entry level into the field. Licensing for apprentice electricians is typically overseen by state or local authorities, involving specific education, training, and examination requirements. An apprentice electrician certificate not only signifies the beginning of one’s journey but also ensures that individuals are adequately prepared to contribute to electrical work standards.
In this comprehensive article, we will delve into the details of the apprentice electrician licensure process, emphasizing exam content, commonalities, and unique aspects across different states. From the structure of the licensure exam to the specific requirements set by state regulatory bodies, aspiring electricians at the entry level will find valuable insights to guide them on their path to licensure.
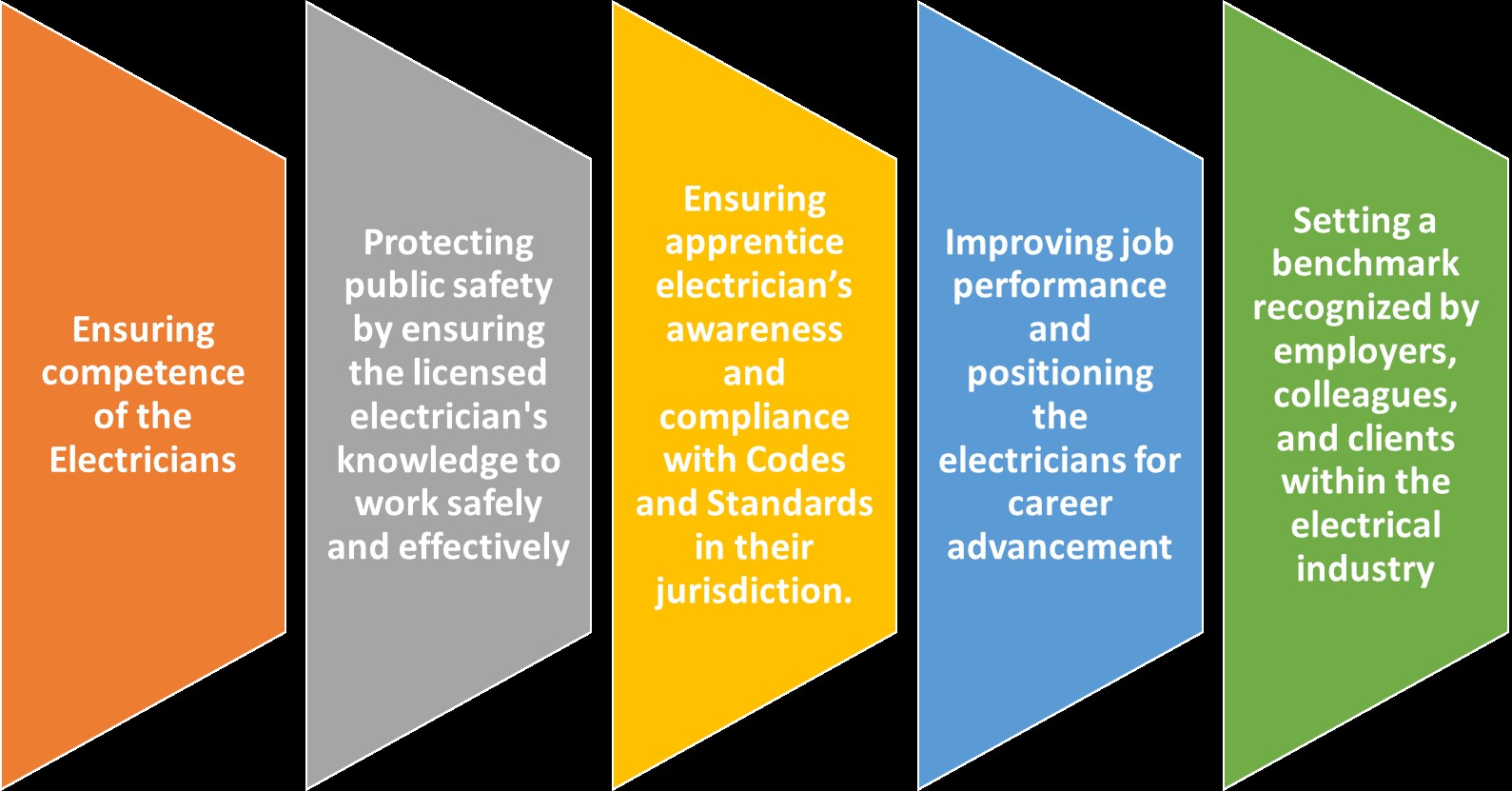
Purpose of the Apprentice Electrician Certification Examination:
The Apprentice Electrician Certification Exam holds significant importance in the electrical trade, serving three essential purposes. Firstly, it ensures public safety by thoroughly assessing competency in electrical codes and safety regulations. Secondly, the exam maintains professional standards within the trade. By indicating proficiency in the craft and requiring a high level of knowledge and skill, it instils confidence in Apprentice Electricians and reinforces the profession’s integrity. Lastly, successful completion of the exam leads to licensure, unlocking pathways for career progression. It broadens job opportunities, enhances salaries, and establishes recognition within the industry, setting the stage for a fulfilling and successful career for qualified individuals. In summary, this rigorous evaluation safeguards the public, maintains professional integrity, and facilitates the pursuit of rewarding careers, ensuring that only the most qualified professionals enter the electrical trade.
The Requirements of the Apprentice Electrician Certification Examination:
There are some educational and experience requirements to be eligible for the Apprentice Electrician. As different States in USA have their own licensure program for electrician, the requirements vary from state to state. Here is a list of general requirements to become an apprentice electrician:
| Educational Background | · High School Diploma or GED plus |
| · Passing of required subjects (high school algebra or post-high school algebra) | |
| Eligibility Requirements | · Minimum of 18 years of age.
· Passing the apprenticeship aptitude test. · Passed drug tests. · State-issued identification. |
In this article, we have included a detailed requirement table for all the states in the USA. The requirements for Apprentice Electrician keep changing, so it is advisable to check with the local licensing authorities to stay updated on the current requirements.
How to Register for the Apprentice Electrician Examination:
| Step | Details | |
| Step 1 | Application | · Find and navigate through the official website of the licensing authority of the state you are trying to be an apprentice electrician from.
· Carefully go through their requirements and check your eligibility. · Submit all required documents and submit your application |
| Step 2 | Fees and Refund Policy | · The fees for Apprentice electrician Licensure exam vary wildly among the states.
· The average range of application fee is $40 to $275. · In some cases, there are additional license fee |
| Step 3 | Verification | · The state licensing authorities reserve the right to verify the documents and certificates you submitted. |
| Step 4 | Notification of Eligibility or Ineligibility | · Once the application is processed, the candidates are notified about their eligibility.
|
| Step 5 | Scheduling the Exam | · In some of the states the licensing authority arranges the written exam themselves, but in most cases, the exam is arranged and overseen by third party organizations.
· After ensuring your eligibility, contact with your respective exam taking authorities to schedule the exam. |
| Step 6 | Appearing the Exam | · Students sit for the exam during their scheduled test time.
· There is usually an open book exam consisting of scored Multiple Choice Questions. The passing score is around 70%. · Candidates will receive an email or printout after the exam indicating their score result.
|
What is the Apprentice Electrician Certification Examination
The career of a electrician can be divided into 3 phases. The first is Apprentice, then comes the journeyman phase and finally master electrician. To enter this journey, one must complete required amount of apprenticeship. The exam for apprentice Electrician is designed to test the basic knowledge acquired during their studies and to assess the individual’s capability to become an electrician. The following table contains general information regarding the Apprentice Electrician examination:
| Question Type | · Multiple-choice: Most exams are primarily composed of multiple-choice questions, with several possible answers for each question. These questions usually test your knowledge of electrical theory, codes, safety regulations, and practical applications.
· True/False: Some exams may also include a smaller number of true/false questions. · Calculations: Some questions may involve basic calculations related to voltage, current, resistance, and load capacity. |
| NO. of Total Question | Most exams consist of 60-100 questions, although some may have slightly more or less. |
| Exam duration | 1.5 to 2 hours |
| Passing Score | The passing score of apprentice electrician is usually 70% to 75% |
| Exam timeline | Exams are offered on a continuous basis. There are no application or registration deadlines. |
| Topics covered | 1. Electrical Theory and Fundamentals:
2. National Electrical Code (NEC) 3. Safety Procedures 4. Tools and equipment 5. Math calculations 6. Reading electrical diagrams and blueprints |
| Delivery Method | · Most exams are now administered electronically on computers, but some states may still offer paper-and-pencil versions.
· Most Apprentice Electrician exams are “open book,” meaning you’re allowed to bring a soft-bound copy of the National Electrical Code (NEC) as a reference during the exam. However, some states may have closed-book exams.
|
Exam Content for the Apprentice Electrician certification exam:
The topics covered in the Apprentice Electrician Exam can vary slightly depending on the specific state or licensing jurisdiction, but generally, they fall into these broad categories:
- Electrical Theory and Principles:
- Basic Electricity: Electron theory, Ohm’s Law, Kirchhoff’s Laws, AC/DC Basics, Electromagnetism
- Electrical Components: Functions and characteristics of resistors, capacitors, inductors, diodes, transistors, transformers, and motors; Circuit analysis with passive and active components.
- Power Calculations: Power formulas and calculations with watts, voltage, and current; Efficiency calculations for electrical devices.
- Code Requirements (National Electrical Code):
- General Safety Requirements: Overcurrent protection devices (fuses, circuit breakers); Grounding and bonding principles; Working clearances and safe work practices.
- Wiring Methods and Materials: Types of conductors (THHN, THW, etc.) and their applications; Proper wiring methods for different locations (concealed, exposed, wet areas); Conduit and box sizing requirements.
- Branch Circuit Calculations: Load calculations for different lighting and appliance circuits; Minimum circuit conductor sizes based on ampacity and voltage drop.
- Specific Equipment Requirements: Requirements for motors, generators, transformers, and other electrical equipment.
- Safety Procedures:
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Selection and proper use of gloves, safety glasses, insulated footwear, and hard hats.
- Lockout/Tagout Procedures: Isolating and de-energizing equipment before work.
- Hot Work Procedures: Safe practices for working on energized electrical systems.
- Emergency Procedures: First aid for electrical shock, fire response, and emergency shutdown procedures.
- Tools and Equipment:
- Hand Tools: Functions and proper use of screwdrivers, pliers, crimpers, wire strippers, and multimeters; Safe handling and storage of hand tools.
- Power Tools: Types of power tools commonly used in electrical work (drills, saws, grinders); Safe operation and maintenance of power tools.
- Testing and Measurement Equipment: Using multimeters, insulation testers, and other equipment for troubleshooting and verification.
- Specialized Equipment: Depending on the job, understanding specialty tools like cable pullers, conduit benders, and wire strippers.
- Math Calculations:
- Basic Algebra: Solving linear equations and manipulating formulas involving voltage, current, resistance, and power.
- Unit Conversions: Converting between different units of measurement (amps, volts, watts, ohms).
- Dimensional Analysis: Applying dimensional analysis to ensure calculations involving length, area, and volume are correct.
- Trigonometry (optional): Basic trigonometric concepts for certain calculations involving angles and electrical components.
- Reading Electrical Diagrams and Blueprints:
- Electrical Symbols and Schematics: Understanding and interpreting common electrical symbols for components and circuits; Following and analyzing wiring diagrams for specific electrical systems.
- Electrical Blueprints: Reading and interpreting electrical plans alongside construction drawings; Identifying electrical components and layouts within the building structure.
- Bill of Materials (BOM): Interpreting lists of materials and equipment needed for specific projects.
The Apprentice Electrician certification exam is conducted by the individual State authorities. This is why the requirements, application and license fees, licensing authority varies from state to state. Most of states don’t have a statewide exam for apprentice electrician certification. Here is a detailed list of this variables for the states which have a certification exam.
| State | Fees | Reciprocity | Licensing authority | |
| Application & Examination | License | |||
| California | $25 | – | Arizona, Nevada, and Utah | Department of Consumer Affairs, Contractors State License Board |
| Delaware | $79 | Maryland, Michigan, North Carolina, and Wyoming | Delaware Division of Professional Regulation, Board of Electrical Examiners | |
| Idaho | $15 | $15 | Alaska, Colorado, Minnesota, Montana, Nebraska, North Dakota, Oregon, South Dakota, Utah, Washington, and Wyoming | Idaho Division of Building Safety |
| Maine | $21 | $25 | Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Oregon, and Vermont | The State of Maine Electricians’ Examining Board |
| Texas | $20 | $70 | N/A | Texas Department of Licensing and Regulation |
What are the Benefits of the Apprentice Electrician Certification?
The Electricians with an apprentice status enjoys a number of benefits:
| Benefits | Details |
| High Demand and Job Security | Electricians are always needed, regardless of the state of the economy. Buildings require constant electrical maintenance and upkeep, and with the increasing focus on renewable energy and smart homes, the demand for skilled electricians is only expected to grow. |
| Strong Earning Potential | Apprentice electricians can earn a good living, with median annual wages exceeding $47,000 in the US. Salaries can vary depending on experience, location, and specialization, but skilled electricians can command even higher salaries. |
| Diverse Career Options | The electrical field offers a wide range of career paths. You can choose to work in residential, commercial, or industrial settings, specialize in areas like solar power or low-voltage systems, or even start your own electrical contracting business. |
| Continuous Learning and Growth | The electrical field is constantly evolving, with new technologies and codes emerging all the time. This means that apprentice electricians have the opportunity to continuously learn and grow throughout their careers. Many employers offer training and development programs to help their electricians stay up-to-date on the latest advancements. |
| Sense of Accomplishment and Problem-Solving | Electrical work provides a tangible sense of accomplishment. Seeing a project come to life, from initial blueprint to functioning electrical system, is a rewarding experience. Electricians also get to solve problems on a daily basis, using their skills and knowledge to diagnose and fix electrical issues. |
| Strong Union Presence | The International Brotherhood of Electrical Workers (IBEW) is a strong union that represents electricians across the country. The IBEW provides its members with benefits such as job security, health insurance, and retirement plans. |
| Flexible work schedules | Many electricians work regular business hours, but some employers offer flexible schedules or the option to work overtime. |
| Sense of independence | Electricians often work independently, which can be appealing to people who like to be their own boss. |
| Making a Difference | Electricians play a vital role in our society. They keep our homes, businesses, and communities safe and functioning. By becoming an electrician, you can make a real difference in the lives of others. |
The Job Prospect after Passing the Apprentice Electrician licensure Examination:
Passing the Apprentice licensure Examination significantly enhances an electrician’s job prospects in the field of electrical system. This achievement opens up a variety of opportunities in different settings and specialties. Here’s an overview of the job prospects available to individuals who have passed the apprentice certification exam:
| Job Prospect | ||
| Diverse Employment Settings | Construction Sites | Build the future brick by brick, working on residential, commercial, and industrial projects, from skyscrapers to schools. |
| Maintenance and Repair | Keep the lights on and systems running smoothly in hospitals, hotels, factories, and other facilities. | |
| Specialized Teams | Join specialized teams focused on specific areas like lighting systems, high-voltage work, or renewable energy installations. | |
| Self-Employment | Chart your own course by starting your own electrical contracting business, serving residential or commercial clients. | |
| Specialization Areas | Low-Voltage Systems | Focus on data networks, communications systems, security systems, and smart home technologies. |
| Renewable Energy | Install and maintain solar panels, wind turbines, and other renewable energy systems. | |
| Controls and Automation | Design and implement automated electrical systems for lighting, HVAC, and other building management functions. | |
| Career Advancement Opportunities | Journeyman & Master Electrician | Gain experience and pass additional exams to qualify for a journeyman and then master electrician license, which allows for project supervision, independent bidding, and higher earning potential. |
| Foreman/Supervisor | Lead a team of electricians on complex projects, managing schedules, budgets, and safety procedures. | |
| Electrical Inspector | Enforce electrical codes and safety regulations by inspecting systems and issuing permits. | |
| Ownership and Entrepreneurship | Build your own successful electrical contracting business, setting your own hours and managing your career on your own terms. | |
| Teaching/Consultant | Share your expertise by teaching students or providing consulting services to engineering firms, architectural teams, or electrical contractors |
The job Duties after Passing the Apprentice Electrician Licensure Examination
After successfully passing the Apprentice certification Examination and obtaining the certificate, electricians become qualified to undertake a variety of responsibilities. The specific job duties can vary depending on the work setting and specialization, but generally include:
| Job Duties | Details |
| Learning and Observing | · Observing and assisting journeyman electricians with various electrical tasks and projects.
· Studying electrical theory and code requirements through apprenticeship classes, textbooks, and online resources. · Learning how to use electrical tools and equipment safely and effectively. · Developing an understanding of safety procedures for working with electrical systems. |
| Assisting and Supporting | · Preparing work areas by setting up ladders, tools, and materials.
· Running errands and fetching supplies as needed. · Cleaning up work areas after projects are completed. · Helping with basic tasks like pulling wire, drilling holes, and mounting boxes. · Following instructions from journeyman electricians carefully and accurately. |
| Performing Simple Tasks | · Cutting and stripping wire to specific lengths and configurations.
· Making basic electrical connections using wire nuts, crimp connectors, and terminal blocks. · Installing electrical components like light fixtures, switches, and receptacles. · Grounding and bonding electrical systems to ensure safety. · Testing and troubleshooting simple electrical circuits for functionality. |
| Additional duties | · Maintaining a clean and organized workspace.
· Communicating effectively with journeyman electricians and other team members. · Being punctual and reliable. · Demonstrating a positive attitude and willingness to learn. |
Approximate Income after Receiving the Apprentice Status:
The income of a certified professional who has passed the Apprentice examination can vary widely depending on several factors such as geographic location, work setting, level of experience, specialization etc. However, some general trends can provide an idea of the potential income for these professionals:
| Level | Income Range | Details | |
| Experience | Entry-Level (0-2 Years) | $35,000 – $45,000 per annum | Reflects typical starting wages for newly certified Apprentice |
| Mid-Level (2-5 Years) | $45,000 – $55,000 per annum | Represents increased earnings with experience and skills development. | |
| Senior-Level (5+ Years) | $50,000+ per annum | Demonstrates potential earnings for highly experienced and sought-after professionals | |
| Location | High-paying states | averages exceeding $60,000 annually | Alaska, Hawaii, California, Washington New York |
| Lower-paying states | averages around $30,000 annually | Mississippi, Arkansas, South Carolina, Alabama, West Virginia | |
| Industry | Industrial and commercial | Higher | Industrial and commercial electricians often earn slightly higher wages than residential electricians. |
| Specialization | Higher | Specialized areas like renewable energy or automation can command premium salaries. | |
| Employer | Unionized electricians | Higher | Typically have higher wages and benefits compared to non-union counterparts |
| Large companies or government agencies | Higher | Large companies or government agencies may offer more competitive salaries than smaller firms. |
A Sequential Guide for Preparing for the Apprentice Electrician Licensure Examination
Preparing for Apprentice Electrician examination requires a step-by-step approach to ensure effective readiness. This sequential guide outlines essential strategies and practices to enhance candidates’ preparation for a successful performance on the exam.
Step 1: Understand the Question Pattern & Time:
Understanding the question pattern is one of the crucial parts of exam preparation. The following key points should be considered to ensure efficient preparation.
The Structure of the Apprentice Electrician Examination:
- Question Type:
Multiple-Choice Questions: The exam largely comprises questions in the format of multiple-choice. Typically, a single correct answer may be identified among a set of four possibilities for each question.
- True/False Questions:
True/false questions are straightforward in format. Candidates are presented with a statement, and they must determine whether the statement is true or false. These questions often assess candidates’ understanding of specific facts or principles.
- Fill-in-the-Blank Questions:
Fill-in-the-blank questions require candidates to provide a missing word, phrase, or no. to complete a sentence or statement. These questions test knowledge of specific terminology and calculations.
- Short-Answer Questions:
Short-answer questions usually require candidates to offer concise written responses to specific questions or prompts. These questions may require candidates to explain concepts, provide solutions to problems, or describe procedures in their own words.
- Number of Questions:
Total Questions: Typically, the examination has approximately 70-100 MCQ questions. In some Apprentice electrician exams, there are also true/false, fill in the blanks or short answer type questions. Number of these question can vary.
- Content Areas:
The Apprentice Electrician exam content is meticulously designed to evaluate electrician’s basic knowledge and applied skills. The content of this exam covers the code editions, electrical safety practices, wiring methods, electrical calculation, practical application etc. Topics like services, feeders, circuits, and their safe grounding and bonding are also included in the exam.
- Duration of the Exam:
Time Allotted: Typically, candidates are allotted a duration of three to five hours in order to finish the examination.
Time Management: Candidates must strategically plan their time to answer all questions, making time management skills crucial.
- Scoring:
Scoring Method: Your raw score is the total number of points you earn on the exam. Each correct answer is awarded its designated point value.
Passing Score: The minimum passing score is usually around 70%, but this can vary slightly between states. Some states may have different passing scores for different sections of the exam.
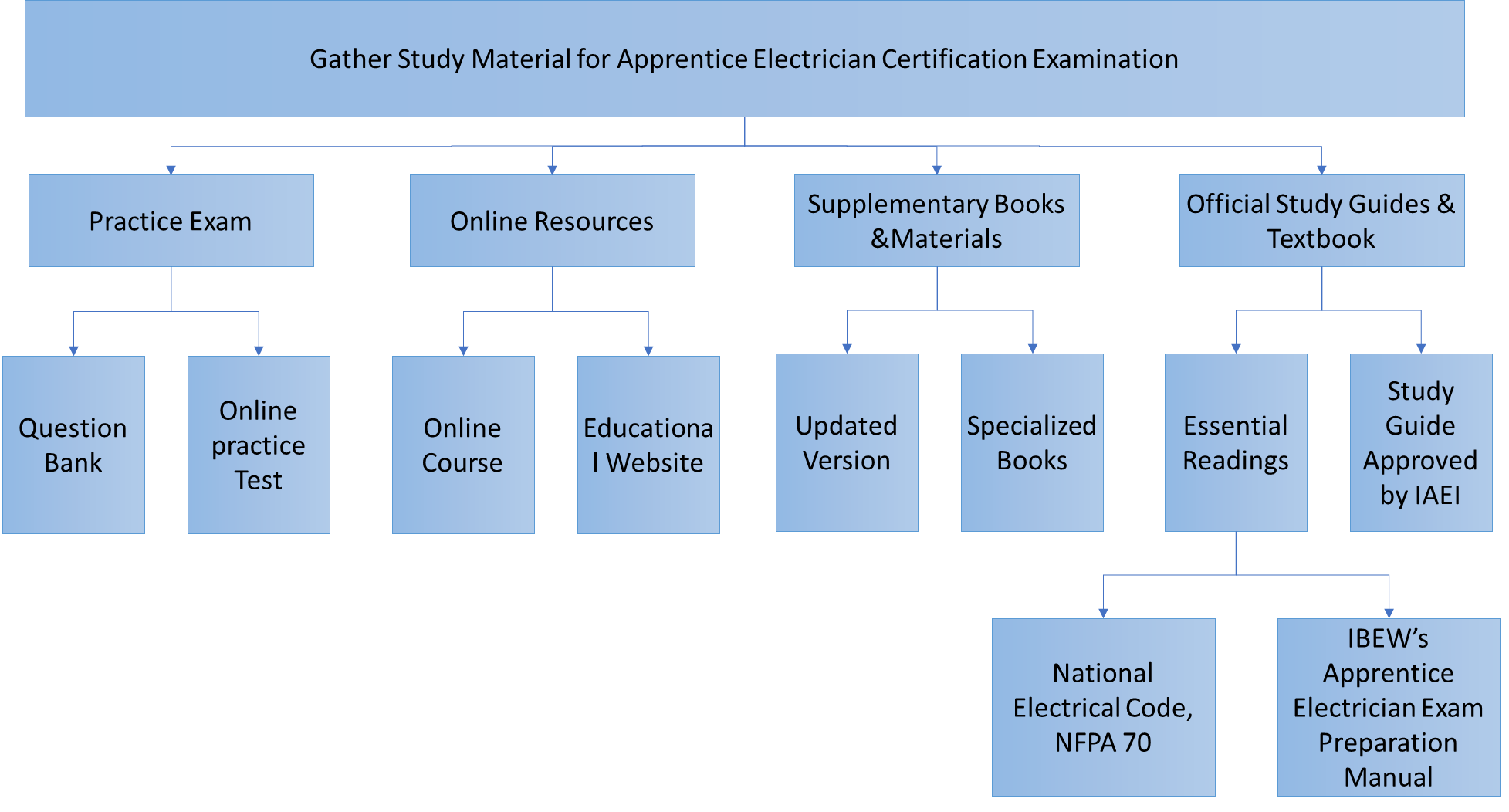
Step 2: Gather your study materials for the examination:
In order to study effectively for the certification, it is crucial to have the necessary study resources. The fundamentals and practical applications necessary for success can be learned from a wide variety of sources. The following is a complete guidebook explaining the procedure of acquiring study materials:
Step 3: Create a study schedule and track your progress
To utilize your time properly and to ensure a thorough preparation, creating a study schedule is a must. Often candidates fail due to poor time management and lack of insight about their own progress. Here is a simple graphical representation of how to create a study schedule and while following it, how to track your progress.
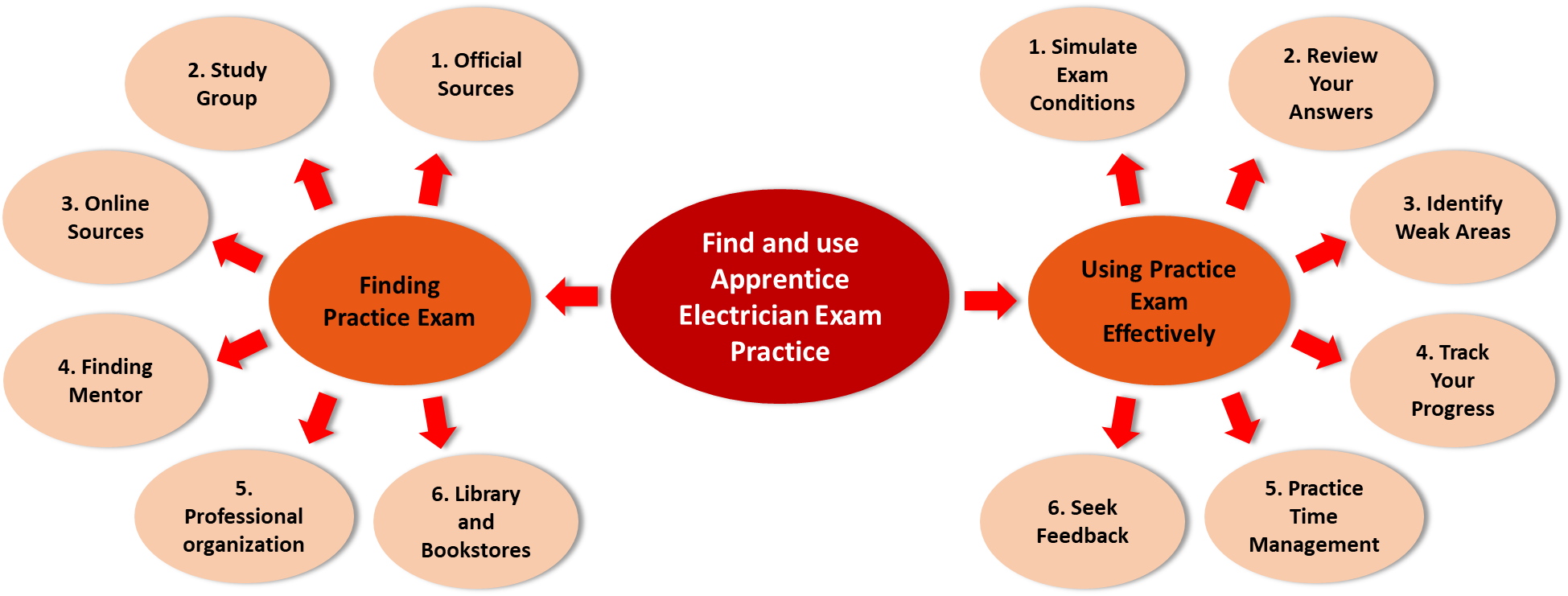
Step 4: Find and Use Mock Test
To prepare yourself thoroughly and to regularly monitor your progress taking Mock Test is one of the most effective ways. But candidates often face some issue about where to find the mock test, and how to properly utilize them. Here is an overview on finding practice exams and using them effectively:
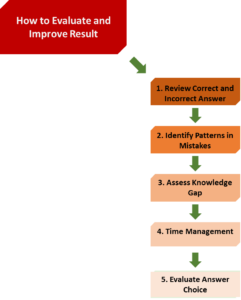
Based on your practice test performances you can evaluate your current level of preparation and find the ways to improve results:
Step 5: Exam Day Preparation for the Apprentice Electrician Certification Examination
The exam day preparation is one of the most significant parts of the preparation process. The following are some of the tips for your last moment preparation.
Complete the easy questions first: On most tests, all questions are valued the same. If you become too frustrated on any one question, it may reflect upon your entire test.
Keep track of time: Do not spend too much time on one question. If a question is difficult for you, mark the answer sheet the answer you think is correct and place a check (✔) by that question in the examination booklet. Then go on to the next question: if you have time after finishing the rest of the exam, you can go back to the questions you have checked. If you simply do not know the answer to a question, take a guess. Choose the answer that is most familiar to you. In most cases, the answer is B or C,
Only change answers if you know you are right. – Usually, your first answer is your best answer.
Relax – Do not get uptight and stressed out when testing.
Tab your Code Book. – References are easier and faster to find.
Use a straightedge. – Prevent getting on the wrong line when referring to the tables in the NEC.
Get a good night’s rest before the exam – Do not attempt to drive several hours to an exam site. Be rested and alert.
Understand the question. – One key word in a question can make a difference in what the question is asking. Underlining key words will help you to understand the meaning of the question.
Use a dependable calculator. – Use a solar-powered calculator that has a battery back-up. Since many test sites are not well-lit, this type of calculator will prepare you for such a situation. If possible, bring along a spare calculator.
Show up at least 30 minutes prior to your exam time. — Be sure to allow yourself time for traffic, etc. when planning your route to the exam location.
Typical Regulations for the Apprentice Electrician Certification Examination
Most licensing agencies outsource their examinations to a testing agency that is a separate entity from the licensing agency. After you get approval from the licensing agency to take the exam, contact the testing agency for their regulations. To ensure that all examinees are examined under equally favourable conditions, the following regulations and procedures are observed at most examination sites:
- Each examinee must present proper photo identification, preferably your driver’s license before you are permitted to take the examination.
- No cameras, notes, tape recorders, pagers, or cellular phones are allowed in the examination room.
- No one will be permitted to work beyond the established time limits.
- Examinees are not permitted any reference material EXCEPT the National Electrical Code.
- Examinees will be permitted to use noiseless calculators during the examination. Calculators which provide programmable ability or pre-programmed calculators are prohibited.
- Permission of an examination proctor must be obtained before leaving the room while the examination is in progress.
- Each examinee is assigned to a seat specifically designated by name and/or number when admitted to the examination room.
General Tips for the Apprentice Electrician Certification Examination
Preparing for and taking the Apprentice Electrician licensure test can be a demanding process. Here are some general tips to guide you through both the preparation phase and the actual exam day:
- Understand the Format and Content: Familiarize yourself thoroughly with the exam format, types of questions, and key content areas.
- Develop a Study Plan: Develop an effective and all-encompassing study schedule. Adhere to your predetermined timetable and modify it accordingly in response to your level of advancement.
- Use a Variety of Study Materials: Integrate diverse study tools, encompassing textbooks, online resources, practise tests, and flashcards.
- Focus on Weak Areas: It is advisable to allocate additional focus to subjects in which one possesses a lesser degree of confidence. Enhance these specific areas with focused study.
- Practice with Mock Exams: It is advisable to engage in a consistent practise regimen that includes the completion of comprehensive examinations of the same duration as the actual test. This approach facilitates the development of familiarity with the time constraints and stress associated with the authentic assessment.
- Join Study Groups: Engage in collaborative efforts with fellow students inside study groups to foster a multifaceted learning environment and receive academic assistance.
- Seek Guidance from Mentors: If feasible, seek guidance and perspectives from individuals who have effectively cleared the apprentice exam.
- Stay Updated: It is advisable to stay informed about any modifications in the examination structure, content, or protocols by regularly consulting the official website of the licensing authority of your state.
Additional Resources for Apprentice Electrician Certification Examination
Official Website: The official website of the state licensing authority provides up-to-date information on this field, including best practices and industry standards.
Online Platforms for Study Materials: Some online platforms offer a range of study materials, including practice exams, tailored for Apprentice Electrician test preparation, and some online platforms Provides comprehensive resources such as practice questions and detailed study guides for aspiring Apprentice Electricians.
Educational Videos and Webinars: Platforms like YouTube host various educational content, including lectures, tutorials, and webinars, specifically focused on topics relevant to the Apprentice Electrician Certification examination.
Mobile Learning Apps: Some of the mobile learning apps allow users to create and access digital flashcards, facilitating memorization and review of key concepts.
A flashcard app can help in efficient retention of information through spaced repetition, ideal for Apprentice Electrician exam preparation.
Academic Journals:
Journal of Counselling & Development: Provides insights into the latest research, theories, and practices in the counseling field.
Counseling Workshops and Seminars: These events offer in-depth knowledge about specialized areas of practice, ranging from introductory to advanced levels, often featuring industry experts.
Study Aids and Specialized Literature: A variety of books, articles, and academic papers covering a wide spectrum of topics relevant to Electrical System content.
Peer Study Groups: Facilitate collaborative learning, allowing candidates to share knowledge, gain new perspectives, and stay motivated throughout their study process.
Professional Mentorship: Established professionals in field who successfully passed the Apprentice examination can offer guidance and support, aiding in both academic and career development.
Conclusion
The apprentice electrician certification exam is a crucial step toward professional mastery in the electrical trade. Beyond assessing technical skills, it emphasizes safety, codes, and ethics. Successfully passing this exam opens doors to career advancement and signifies a commitment to industry standards and public safety. As technology advances, this certification remains a testament to the dedication and professionalism required in the dynamic field of electrical work.
Aspiring candidates embarking on the journey to obtain the Apprentice Electrician certification can follow a step-by-step preparation guide that includes mastering the relevant codes and familiarizing themselves with necessary knowledges. This guide serves as a roadmap for success, providing a structured approach to tackle the challenges posed by the examination and the demanding nature of Electrician’s career.
Ultimately, achieving the Apprentice title signifies not just a personal accomplishment but a commitment to the safety and reliability of electrical system. It is a recognition of capability and a mark of professionalism that benefits both electricians and the communities they serve. As the demand for skilled electricians continues to grow, the Apprentice Electrician Certification Examination stands as a valuable credential, opening doors to opportunities and contributing to the overall enhancement of electrical safety standards.